
Intro
While initially it may seem a bit dull, this policy is crucial to understand if you are seeking certification as a nationally registered paramedic (NRP). In this article, we will break down the scope of practice, the steps to attain your NRP certification initially or if you currently hold a state certification only, and how to recertify as an NRP.
Paramedic Description
The NRP may work in an in-hospital or pre-hospital setting and may be responsible for responding to, triaging, and/or treating sick and injured patients. Paramedics have more advanced training and are therefore able to provide a wide range of care and treatment and often form differential diagnoses based on a thorough patient assessment. Because of this, NRPs may respond to emergent and non-emergent calls and interfacility transfers. Additionally, paramedics play a role in public prevention and education regarding medical concerns, mental health, and safety issues1.
Paramedics are a crucial part of the EMS response and public safety system. They are responsible for utilizing equipment to provide interventions in lifesaving care to patients or specialized care during interfacility transfers1.
Prerequisites
The following outlines the education requirements to attain NRP certification1:
Hold a valid EMT or AEMT state license.
- Have successfully completed a paramedic program accredited by the CAAHEP that adheres to or exceeds the NEMSES within 2 years from the start date with verification from the Program Director
- Meet all standards set forth by the CoAEMSP Recommended Student Minimum Competency Matrix
- Successfully complete the application and payment portion clearly showing course standards have been met
State Licensure to National Certification
If you currently hold state licensure but are seeing national certification, you will need the following to test for national certification:
- Valid and active Paramedic state licensure or higher (or that which is recognized as equivalent per state guidelines)
- Completion of the required 30 hours of continuing education per the national component of the National Continued Competency Program (NCCP) within the last 2 years
- Application and payment
What if my certification has lapsed?
This is treated similarly to those who hold state, but not national, licensure. The two primary differences are that the candidate must complete all 60 hours of continuing education per the NCCP model and a skill evaluation per NREMT guidelines.
How long is my NRP certification valid?
Once again, the answer is 2 years. However, there is a caveat - all NREMT certifications expire on March 31st, 2 years following your date of certification completion
If you completed your certification between July 1st and December 31st, your licensure will be valid until March 31st, three years in the future1. See our helpful chart below:
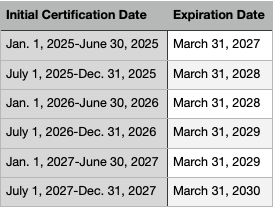
Recertification
Once you’re certified, you can go out into the world and practice as an EMT! However, if you want to keep practicing as an NRP you’ll need to recertify BEFORE your expiration date (see table above or your NREMT card) using one of two methods listed below:
Method 1: Continuing Education (most popular method)
The continuing education (CE) requirement for Paramedic recertification consists of 60 credits, all of which must be State EMS Office or CAPCE-approved. The following shows the breakdown of these CE credits:
- 30 Credits for the aforementioned National Continued Competency Program (NCCP)
- 15 Credits that satisfy the Local requirement for the NCCP
- 15 Credits that satisfy the Individual requirement for the NCCP
This means that you’ll need to complete 60 hours of continuing education between your initial certification and expiration dates. Many things can count as continuing education, including applicable college courses and CAPCE-accredited continuing education classes, such as those offered by EMT-CE!
If that sounds like a lot to navigate and manage, our recertification bundles are specifically designed to meet all of the NREMT’s standards, which makes it really simple!
Method 2: Examination
The other option for valid recertification is successful completion after the FIRST attempt at the National Registry Paramedic cognitive exam within one year of certification expiration.
After one of these methods of recertification has been completed, the candidate must pay the required fees and paperwork.
The final step is required for any candidate seeking “ACTIVE” provider status. A local “Training Officer” must verify the candidate meets the knowledge and skills required by an NRP.
NOTE:
All individuals seeking EMS certification must adhere to all components of the Code of Conduct set forth by the NREMT.
Next Steps
After completing the prerequisites described above, a candidate can take the NREMT exam. If you have more questions about the cognitive or written portion of the exam, we’ve recently written articles on the NREMT cognitive exam format that are worth a read!
Visit EMTprep.com for study guides, flashcards, videos, interactive exercises, practice quizzes, and even a beta computer adaptive test (CAT) exam, all geared toward helping you pass the NREMT. If you follow our recommended study path using our “Readiness Score,” we guarantee you will pass the NREMT!
If you’re already certified and looking for those continuing education hours, EMT-CE.com has you covered! We have everything you need to meet your national AND state recertification requirements.
For the full policy, check out the NREMT's "Certification Scheme – Paramedic."
- 1. Certification Scheme – Paramedic +. (n.d.). https://www.nremt.org/Policies/Certification-Policies/Certification-Scheme-%E2%80%93-Paramedic https://www.nremt.org/Policies/Certification-Policies/Certification-Scheme-%E2%80%93-Paramedic
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time


