
Intro
Maybe you stumbled upon the EMT Certification Scheme policy because you’re a newly minted EMT, or you’re just exploring the idea of becoming an EMT. If that’s you, welcome to the field of EMS! This article will explain what it takes to get certified (and eventually recertified) as an EMT.
EMT Description
The certification scheme starts with an understanding of what an EMT does. The NREMT offers a lengthy explanation, but the gist is that EMTs respond to assist with emergent or non-emergent evaluation and transport of patients, usually as part of a team. The EMT’s role could be supportive of another provider with a higher level of training, or the EMT may be the highest-trained provider available, even providing supervision to others with lower levels of training (such as Emergency Medical Responders or first aid-trained individuals). While EMTs may practice in many settings, this quote sums it up nicely: “EMTs can be the first to arrive on scene; they are expected to quickly assess patient conditions, provide stabilizing measures, and request additional resources, as needed1.”
The role of an EMT is then further defined as a provider who works within an EMS, community health, or public safety system and functions under “medical oversight” (think protocols, standing orders, or supervision by a physician). The EMT uses the equipment available to them to manage life threats and address patients' medical or psychological needs. In general, the job of an EMT is to deliver patients from wherever they are found to definitive medical care (usually a hospital)1.
Prerequisites
The following outlines the education requirements to attain NREMT certification1:
- Successful completion of a state-approved EMT course within 2 years from the start date with verification from the Program Director
- Successful completion of a state-approved psychomotor skills assessment within 2 years of seeking certification
- Successful completion of a state-approved cognitive exam within 2 years of seeking certification
If it’s been over two years since your EMT course, and you don’t have a state EMT license (or your license has lapsed), you’ll need to complete 40 hours of continuing education per the National Continued Competency Program’s (NCCP) requirements.
Again, this must be completed in a 2-year period.
How long is my EMT certification valid?
Once again, the answer is 2 years. However, there is a caveat - all NREMT certifications expire on March 31st, 2 years following your date of certification completion
If you completed your certification between July 1st and December 31st, your licensure will be valid until March 31st, three years in the future1. See our helpful chart below:
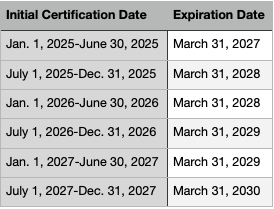
Recertification:
Once you’re certified, you can go out into the world and practice as an EMT! However, if you want to keep practicing as an EMT, you’ll need to recertify BEFORE your expiration date (see table above or your NREMT card) using one of two methods listed below:
Method 1: Continuing Education (most popular method)
The continuing education (CE) requirement for EMT recertification consists of 40 credits, all of which must be State EMS Office or CAPCE-approved. The following shows the breakdown of these CE credits:
- 20 Credits for the aforementioned National Continued Competency Program (NCCP)
- 10 Credits that satisfy the Local requirement for the NCCP
- 10 Credits that satisfy the Individual requirement for the NCCP
This means that you’ll need to complete 40 hours of continuing education between your initial certification and expiration dates. Many things can count as continuing education, including applicable college courses and CAPCE-accredited continuing education classes, such as those offered by EMT-CE!
If that sounds like a lot to navigate and manage, our recertification bundles are specifically designed to meet all of the NREMT’s standards, which makes it really simple!
Method 2: Examination
The other option for valid recertification is successful completion after the FIRST attempt at the National Registry EMT cognitive exam within one year of certification expiration.
After one of these methods of recertification has been completed, the candidate must pay the required fees and paperwork.
The final step is required for any candidate seeking “ACTIVE” provider status. A local “Training Officer” must verify the candidate meets the knowledge and skills required by an NREMT.
NOTE:
All individuals seeking EMS certification must adhere to all components of the Code of Conduct set forth by the NREMT.
Next Steps
After completing the prerequisites described above, a candidate can take the NREMT exam. The NREMT doesn’t have the psychomotor (skills-based) portion of the exam, just a cognitive (computer-based or “written”) exam. If you have more questions about the cognitive or written portion of the exam, we’ve recently written articles on the NREMT cognitive exam format that are worth a read!
Visit EMTprep.com for study guides, flashcards, videos, interactive exercises, practice quizzes, and even a beta computer adaptive test (CAT) exam, all geared toward helping you pass the NREMT. If you follow our recommended study path using our “Readiness Score,” we guarantee you will pass the NREMT!
If you’re already certified and looking for those continuing education hours, EMT-CE.com has you covered! We have everything you need to meet your national AND state recertification requirements.
For the full policy, check out the NREMT's "Certification Scheme – Emergency Medical Technician."
- 1. Certification Scheme – Emergency Medical Technician +. (n.d.). https://nremt.org/Policies/Certification-Policies/Certification-Scheme-%E2%80%93-Emergency-Medical-Technician https://nremt.org/Policies/Certification-Policies/Certification-Scheme-%E2%80%93-Emergency-Medical-Technician
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time


