In this article, we are going to discuss some common ECG interpretations that are beneficial for EMTs to understand in the field. Although performing electrocardiographic rhythm interpretation is outside the EMT-B scope of practice, having a basic understanding can be advantageous during calls so that you have a better grasp of what is going on with the patient. REMEMBER: ALWAYS FOLLOW YOUR LOCAL PROTOCOLS!!
First, let's look at a normal heart rhythm, then we can examine some common morphologies that may indicate the need for treatment.
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
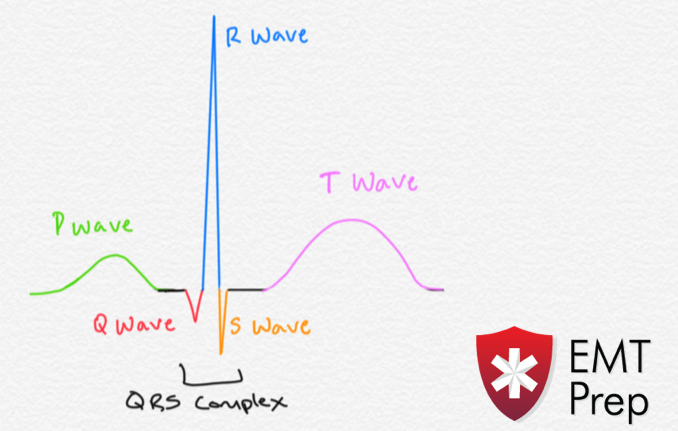
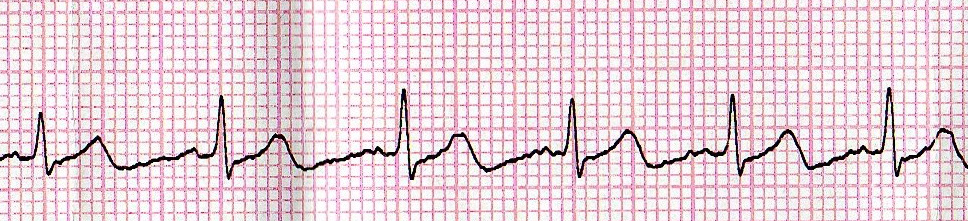
Normal sinus rhythm is the natural-looking rhythm in a healthy heart. It is marked by 3 components: P-wave, QRS-complex, and T-wave. The P-wave corresponds to the electrical activity as the atria contract (depolarize). The QRS-complex corresponds to the electrical activity as the ventricles contract, and the T-wave corresponds to the electrical activity as the ventricles repolarize (or recover). The rhythm can be fast, indicating tachycardia, or slow, indicating bradycardia.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
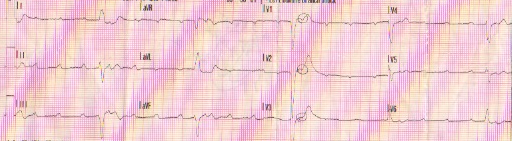
Supraventricular tachycardia is an extremely fast heart rhythm, usually above 150 beats/min. When the heart beats above 150 beats/min, the P-waves, if present at all, become unreadable as they are obscured by the T-wave from the preceding heartbeat. When the heart beats this fast, its preload is diminished, decreasing cardiac output. Patients experiencing SVT may complain of chest pain or just a “funny feeling” in their chest. They may show symptoms such as cool, pale skin, diaphoresis, hypotension, altered mental status, or they may show no symptoms at all.
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
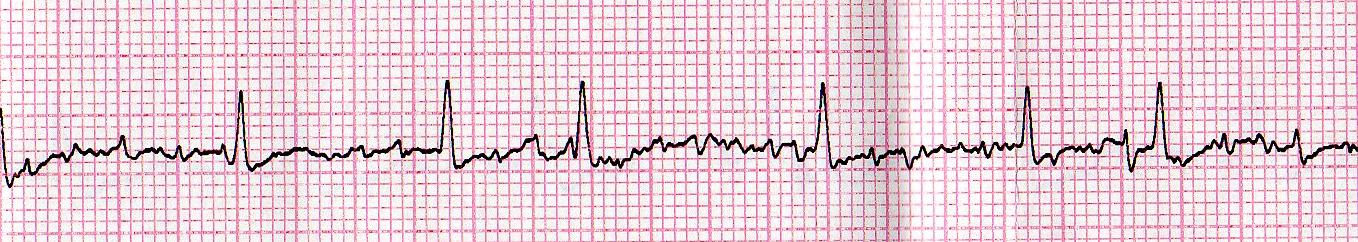
Atrial fibrillation is a rhythm in which the atria do not fully contract, but rather quiver uncontrollably. As a result, there is no defined P-wave and the overall heart rhythm looks "irregularly irregular." This rhythm is common in elderly people and is usually a serious sign of a heart problem. The major concern with a-fib is that blood has a tendency to clot in the atria which can lead to a stroke later on. Patients who have this heart rhythm are usually on some sort of blood thinner to prevent clots from forming.
Ventricular Tachycardia (V-Tach)
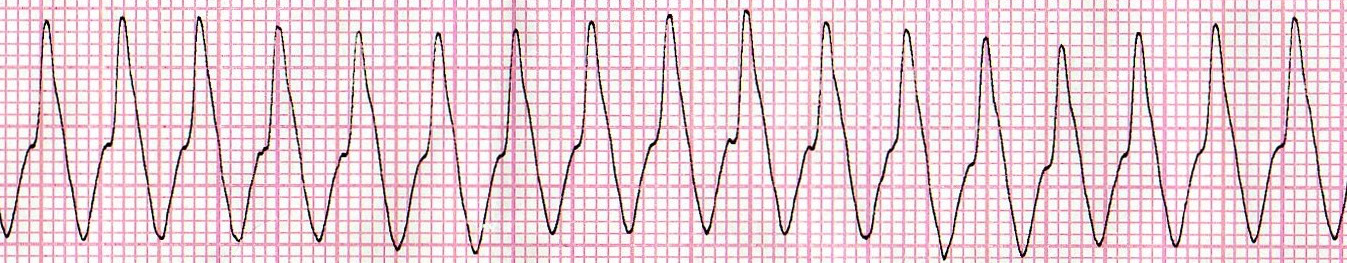
Sustained ventricular tachycardia is a type of tachycardia that arises from improper electrical conduction of the heart. In this rhythm, the ventricles are the main pumping chambers. This is a very serious heart complication and should be treated immediately. The ventricles are contracting too fast for the heart to adequately pump blood to the body and it can lead to ventricular fibrillation or failure if not treated.
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time


