Back to all articles
article
Updated Jun 2, 2022
Cardiac Tamponade
Updated Jun 2, 2022
Cardiology and Resuscitation
Cardiac Tamponade Study Guide
In EMS, chest pain and chest injuries are some of the most critical and time-sensitive patients we encounter. Cardiac Tamponade is no different.
What is it?
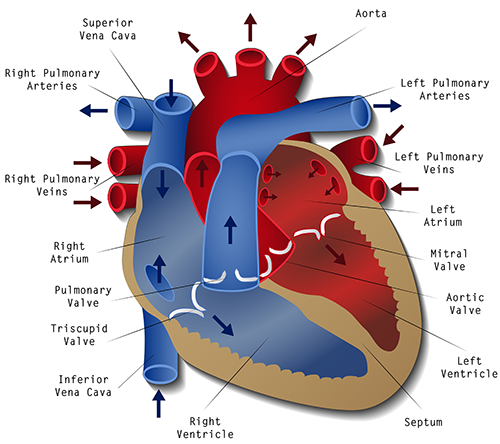
- Cardiac tamponade is a buildup of fluid in the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart which impairs the heart’s ability to contract and the ventricles to fill normally. When the ventricles are not allowed to fill as they want, we see a decrease in stroke volume, a drop in cardiac output, and visible signs of shock.
- A series of events occur once the pericardium begins to fill with fluid:
- The fluid around the heart begins compressing the wall of the heart itself
- This compression does not allow the heart's chambers to expand, which prevents adequate filling
- The inability to fill causes an internal traffic jam with blood
- The back-up of blood means inadequate gas exchange at the lungs and poor perfusion of all tissues
How does it occur?
- Cardiac tamponade often occurs as a result of trauma to the chest. Trauma can come from external, blunt, or penetrating forces to the chest wall itself, or it can come indirectly from things like surgery. Myocardial infarctions can also cause cardiac tamponade when they result in cardiac rupture. Further, there are different types of infections that can cause cardiac tamponade.
What can we do about it?
(These are given as a general rule of thumb, ALWAYS FOLLOW YOUR LOCAL PROTOCOLS!)
- Apply high concentration oxygen
- Consider C-spine and full spinal immobilization if suspected trauma
- Check vital signs every 5 minutes
- Monitor ECG rhythms for any signs of arrhythmia
- Ensure the patient is kept warm
- Rapid transport and avoid things that will delay transport to an appropriate facility
- Establish IV access and administer fluids as needed
- Pericardiocentesis is the definitive treatment that few EMS personnel can perform. This is a procedure where a needle is inserted into the pericardial sac so that the excess fluid can be removed
Extra Resources
- Check out our video on Beck’s Triad
- Beck’s Triad: Low arterial blood pressure, distended neck veins, and muffled heart tones
Studying for the NREMT?
We've helped over 200K+ students pass their NREMT, all for just $39/month
Need to recertify?
The easiest way to get your CE hours, 100% online.
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time