Once you understand the basics of capnography, it is helpful to consider some common waveforms and how to interpret them. As you may know, a normal waveform takes the shape of a square with an end-tidal measurement (height) between 35-45 mmHg and a baseline of zero. Below, we will see how changes in ventilation change the waveform shape and end-tidal measurement.
HYPERVENTILATION
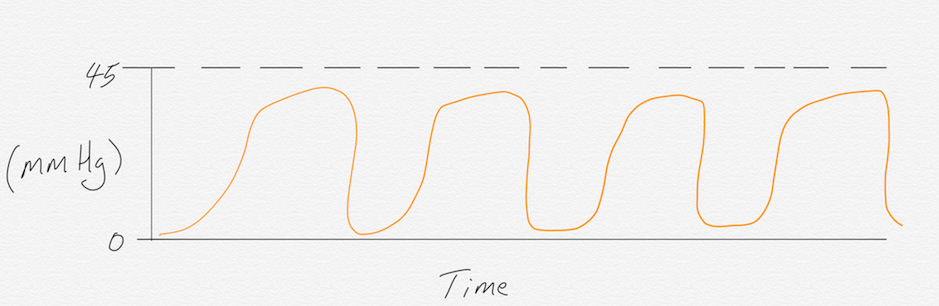
The trademark sign of hyperventilation is a CO2 measurement of less than 35 mmHg. This is because hyperventilation causes a decreased CO2 level in the body due to excess elimination from rapid breathing. The shape of the waveform is typically normal, but with each of the four phases shortened. Causes of hyperventilation can be anxiety, metabolic acidosis, and excessive exercise, among a myriad of other things.
HYPOVENTILATION
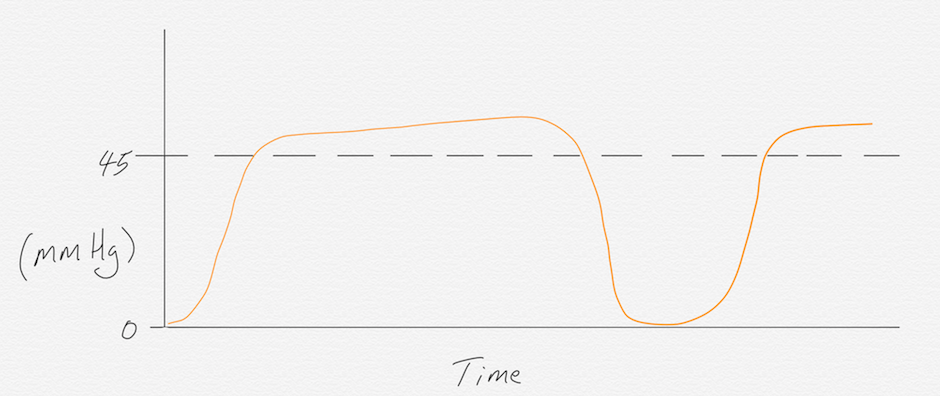
The trademark sign of hypoventilation is a CO2 measurement greater than 45 mmHg. This is because hypoventilation causes an increased CO2 level in the body due to the inadequate elimination of CO2. The shape of the waveform typically has a rapid phase II, prolonged phase III, and rapid phase IV.
ASTHMA/EMPHYSEMA/COPD
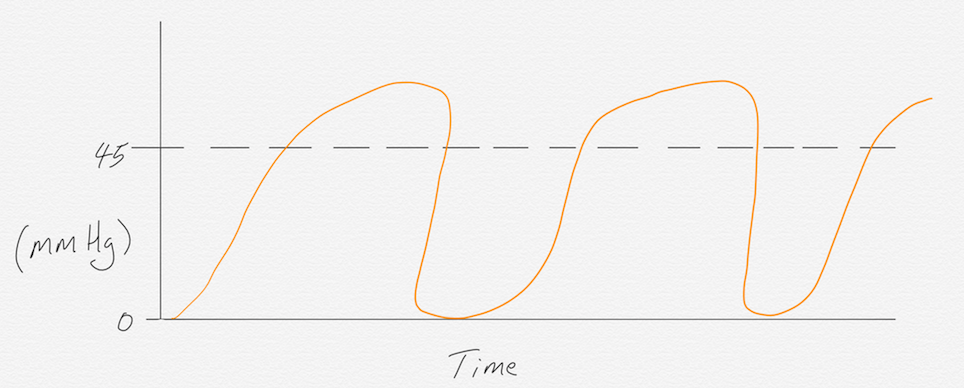
Emphysema, asthma, and COPD cause bronchospasms that result in the “shark fin” waveform morphology as phase II curves into phase III. This morphology represents the work of breathing these patients exhibit as they struggle to exhale completely. In severe cases, air trapping will occur causing a buildup of CO2 in the lungs, which will result in end-tidal measurements greater than 45mmHg.
CO2 REBREATHING
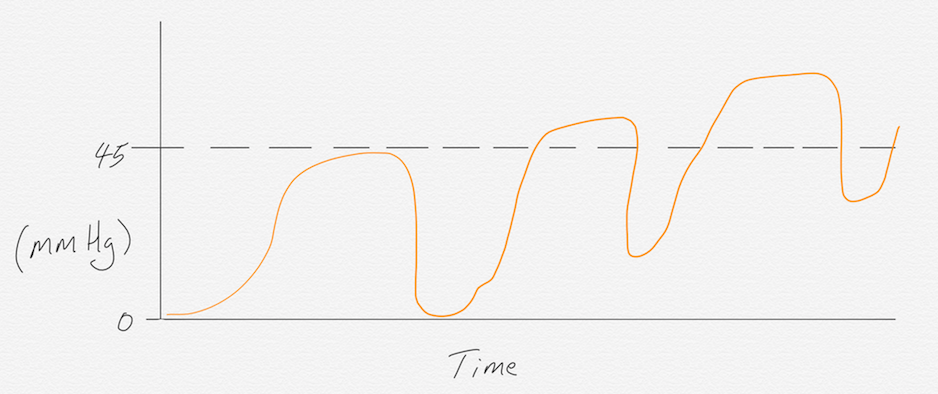
This waveform reading is caused by the rebreathing of exhaled gas or a valve malfunction on a BVM.
CPR APPLICATION WITH ROSC
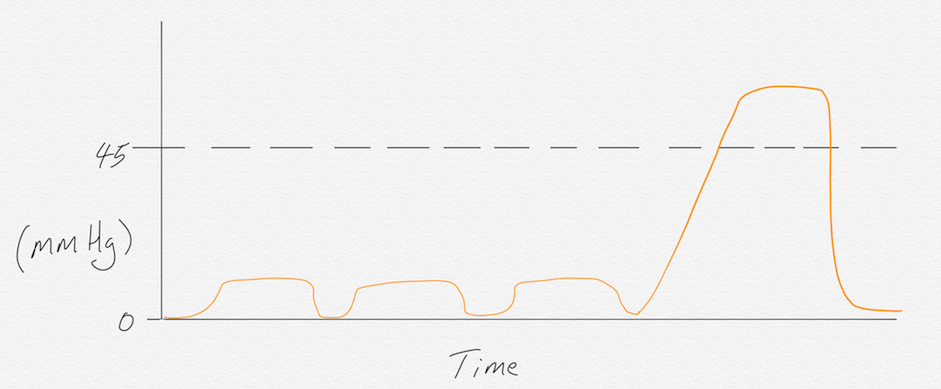
Waveform capnography can be used to assess the quality of compressions during a cardiac arrest event. Good CPR should yield a reading of at least 10 mmHg or more. If the capnography reading is less than 10, the quality of compressions needs to improve, the person doing compressions is fatigued and needs to swap out with someone else, or the patient has been deceased for an extended period of time. If during the code, the end-tidal reading rapidly increases above 45 mmHg, return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) has been achieved. This spike in end-tidal occurs because the body has been accumulating CO2 due to reduced perfusion from only compressions. Suddenly the heart kicks in and begins perfusing blood at a greater rate, releasing the built-up CO2.
CURARE CLEFT
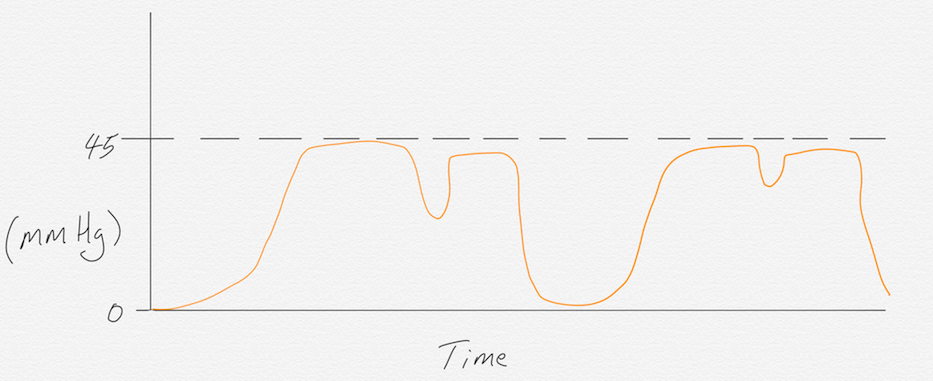
Curare cleft is recognized by a sudden dip in the waveform during phase III. This is seen in patients who are being ventilated through an ET tube. The “cleft” indicates that the neuromuscular blockade is wearing off and the patient is making an effort to breathe on their own. If this waveform is seen, you have roughly 2-3 minutes to administer another dose of neuromuscular blockade before the patient emerges from paralysis.
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time


