Med Math 101: The Basics Everyone Should Know
Trust us, you need to know this stuff…
The Units of Measurement
In the EMS setting, we worry about three metric units of measurement…
- Grams (g) – weight
- Meters (m) – distance
- Liters (L or l) – volume
Attached to these units of measurement will be one of the following…
- Kilo – one thousand (1,000)
- Centi – one hundredth (.01)
- Milli – one thousandth (.001)
- Micro – one millionth (.000001)
Now let’s combine the two…
- Kilogram (kg)
- Gram (g)
- Milligram (mg)
- Microgram (mcg)
- Centimeter (cm)
- Liter (L)
- Milliliter (ml)
Metric System Practice Problems
Tip: If you’re going from a smaller unit to a larger unit, move the decimal point to the left.
1. Milligrams to Grams (move the decimal 3 points to the left)
- 740mg = .740g
- 2mg = .002g
- 100mg = .1g
2. Grams to Kilograms (move the decimal 3 points to the left)
- 4000g = 4kg
- 750g = .75kg
- 93500g = 93.5kg
3. Micrograms to Milligrams (move the decimal 3 points to the left)
- 250mcg = .25mg
- 500mcg = .5mg
- 1000mcg = 1mg
Tip: To convert from a larger to a smaller unit, move the decimal point to the right.
1) Grams to Milligrams (move the decimal 3 points to the right)
- 50g = 50000mg
- 7500 = 7500000mg
- 3g = 3000mg
2) Kilograms to Grams (move the decimal 3 points to the right)
- 35kg = 35000g
- 250kg = 250000g
- 7kg = 7000g
1kg ———- 1,000g ———- 1,000,000mg ———- 1,000,000,000 mcg
Converting Pounds to Kilograms
As a paramedic, you must quickly convert a patient’s weight from pounds to kilograms. As you know, this is done for any medication with weight-based dosing. When the pressure is on, you will need a fast and easy-to-remember way to do your conversions.
- You have a 200lb patient. You need to convert their weight to kilograms so you can administer a Lidocaine bolus at 1.5mg/kg
- Cut the patient’s weight in half… 200lb / 2 = 100
- Take 10% of that number and subtract it from itself… 100 / 10 = 10. 100 – 10 = 90kg
- You have a 40lb pediatric patient. You need to convert their weight to kilograms to administer Succinylcholine at 2mg/kg.
- Cut the patient’s weight in half… 40lb / 2 = 20.
- Take 10% of that number and subtract it from itself… 20 / 10 = 2. 20 – 2 = 18kg
Converting Kilograms to Pounds
Occasionally, you may need to convert kilograms to pounds. Here is a quick and easy way to do so:
- Multiple the patient’s weight in kilograms by 2… 60kg x 2 = 120
- Take 10% of that new number and add it to itself… 120/10 = 12. 120 + 12 = 132lb.
Medication Concentrations & Bolus Doses
The Paramedic’s bread and butter
Glossary of Terms
While most of these terms are self-explanatory, let’s define them, so there is no confusion.
- Desired Dose: the dose we want to administer to the patient
- Total Drug Amount: the total amount of a drug within its container
- Total Drug Volume: the amount of fluid within a drug’s container
- Administered Volume: the amount of fluid (mL) we will administer to a patient
Medication Concentrations
Fortunately for EMS professionals, most of our medication concentrations are expressed as a unit of weight per volume. Usually, you will see this expressed on a medication as either g/ml, mg/ml or mcg/ml. You can find this number on the medication box or vial.
So let’s put this all together…
- Let’s set up this calculation for the most typical concentration we see in the field: mg/ml.
Concentration (mg/ml) = Total Drug / Total Volume
Fill in the numbers we see on Furosemide (Lasix)
Furosemide Concentration = 40mg / 10 ml = 4mg/ml
Sometimes concentrations are expressed as a percentage (Dextrose 50%, Lidocaine 2%). There is a very simple way to solve this so don’t make this too complicated! Let’s look at Lidocaine 2%.
- Take the percentage number (2%) and make it grams… 2% = 2 grams
- Take the number of grams and place it over 100mL:
2g / 100mL = 2000mg / 100mL = 20mg/mL
(This is the concentration seen on a prehospital Lidocaine vial)
Feel like trying Dextrose 50%? Ok, lets do it.
- Take the percentage number (50%) and make it grams… 50% = 50 grams
- Take the number of grams and place it over 100mL:
50g / 100mL = 50000mg / 100mL = 500mg / 1mL = 0.5g/mL
(This is the concentration seen on a D50% box)
Bolus Medications
When you administer a bolus of a medication, you are giving a specific amount all at once. This is different from a drip, where a certain amount of drug is administered slowly over a period of time. Paramedics usually administer medication by bolus instead of drip. Every medication has a solute and a solution, leading to a concentration. It is up to you as a paramedic to determine how much you need to administer to deliver the correct amount of medication to your patient.
Depending on the information you have, you can use one of two equations to calculate how many mL of a drug you will need to administer:
X (mL to be given) = (Total Volume x Desired Dose) / Total Amount of Drug
X (mL to be given) = Desired Dose / Concentration
Let’s try a bolus medication calculation…
- You need to administer 15mg of Diltiazem to a patient. The Diltiazem is supplied in a vial that contains 25mg in 5mL. How many mL will you need to draw up?
Volume (mL to be given): X
Total Amount of Drug: 25mg
Total Volume: 5mL
Desired Dose: 15mg
X (mL to be given) = (Total Volume x Desired Dose) / Total Amount of Drug
Fill in known information to equation:
X (mL to be given) = (5mL x 15mg) / 25mg
X (mL to be given) = 75mL / 25 (mg cancels out)
X (mL to be given) = 3mL
Your patient in cardiac arrest requires 300mg of Amiodarone per 2010 ACLS guidelines. The Amiodarone is supplied in a pre-filled syringe that contains 450mg in 3mL. How many mL will you need to draw up?
Volume (mL to be given): X
Concentration: 450mg / 3mL = 150mg/mL
Desired Dose: 15mg
X (mL to be given) = Desired Dose / Concentration
Fill in known information to equation:
X (mL to be given) = 300mg / (150mg/mL) (mg cancels out)
X (mL to be given) = 2mL
Medication administration: Drip Sets
IV Drip Functions:
- Maintenance Drip: A maintenance drip allows you to maintain the therapeutic levels of a drug after giving a bolus medication. Maintenance drips are usually dripped in at a specified rate (15mL/hr) instead of a specified dose (300mg total).
- Bolus Over Time: Some treatments must be administered over a certain length of time. Take, for instance, amiodarone given for stable ventricular tachycardia with pulses. According to current ACLS guidelines, 150mg of Amiodarone should be given over 10 minutes. Amiodarone often comes in vials that contain 150mg of Amiodarone in 3mL. How are you supposed to give 3mL over 10 minutes? By mixing it in a 100mL IV bag of normal saline and starting an IV drip!
- Drip to Decrease Potency Effects: Some of the drugs we give are very potent and can cause adverse reactions and side effects that need to be avoided in certain circumstances. For example, Nitroglycerin works to relieve chest pain but can cause a patient’s blood pressure to drop dangerously low. The sublingual dose is .4mg (400mcg) and is administered all at once. A nitroglycerin drip is started at 10mcg, which means that 1/40 of a sublingual dose is given over 1 minute! By administering Nitroglycerin via drip, you can titrate the drug to relief of pain and reduce the negative effects it has on blood pressure.
IV Drip Components:
- IV Bag (solution to be administered): an IV bag is a bag of solution to be administered to the patient. The bag can be regular fluid (normal saline) or it can have a drug mixed in with it. Some IV drugs come in premixed IV bags (Lidocaine, Dopamine) while others require premixing prior to administration (Amiodarone, Epinephrine).
- Drip Set: an IV drip set connects the IV bag to the actual IV catheter, allowing the solution to be administered to the patient. A drip set is categorized by how many drips it takes to administer one mL of solution. There are two types of IV drip sets – macro and micro. Macro drips sets produce larger drops, requiring 10-15 drips/mL (depending on the manufacturer). Micro drip sets produce smaller drops, requiring 60 drips/mL.
- Choosing a Drip Set: macro drip sets (10-15 gtt/mL) are generally used for fluid administration because they allow for quick administration of large amounts of volume. Micro drip sets (60 gtt/mL) are generally used for medication administration because a medication drip usually requires small amounts of medication to be administered over time.
Note: The abbreviation for drip rate is drips/minute, or gtt/min.
IV Drip Formulas
There are two formulas that can be used when calculating drip rates. One formula is the general formula for calculating drip rates and the other is used for calculating specific amounts of fluid administration over time.
General formula: a certain amount of drug (with a specified concentration) to be given at a desired dose
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
X: calculated drip rate, expressed in drips/minute (gtt/min)
Desired Dose: total amount of drug needing to be administered, usually defined as a rate (ex. 450mcg/min)
Drip Set: number of drips required to produce one mL of solution (ex. 60gtt/mL)
Drug Concentration: amount of drug in vial/bag (ex. 400mg/250mL)
Fluid administration formula: administration of a specified volume of solution given over time
X = (Total Volume x Drip Set) / Total Time
X: calculated drip rate, expressed in drips/minute (gtt/min)
Total Volume: total amount of volume needing to be administered (ex. 10 Liters of NS)
Drip Set: number of drips required to produce one mL of solution (ex. 15gtt/mL)
Total Time: total amount of time that fluid needs to be administered over (ex. 8 hours)
So how do I calculate a drip rate using all of that information…
You are preparing to administer a nitroglycerin drip for your patient. You need to administer 40mcg/min of Nitroglycerin. If you are using a 60-drop/mL drip set, what should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Desired Dose: 40mcg/minute
Drip Set: 60-drop/mL
Drug Concentration: 200mcg/mL
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
Fill in known information to equation:
X (calculated drip rate) = (40mcg/minute x 60-drop/mL) / 200mcg/mL
X = 2400 (mcg & mL cancel out) / 200
X = 2400 / 200 = 12 gtt/minute
You are preparing to administer an Epinephrine drip for your patient. You need to administer 2mcg/min of Epinephrine. If you are using a 60-drop/mL drip set, what should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Desired Dose: 2mcg/minute
Drip Set: 60-drop/mL
Drug Concentration: 1mg/250mL (1000mcg/250mL = 4mcg/mL)
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Desired Dose X Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
Fill in known information to equation:
X (calculated drip rate) = (2mcg/minute x 60-drop/mL) / 4mcg/mL
X = 120 (mcg & mL cancel out) / 4
X = 120 / 4 = 30 gtt/minute
Let’s calculate the drip rates for some fluid administration…
You have been ordered to administer 1L of Normal Saline during your 1-hour transfer. If you are using a 15-drop/mL drip set, what should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Total Volume (mL to be given): 1000mL
Drip Set: 15-drop/mL
Total Time: 60 minutes
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Total Volume x Drip Set) / Total Time
Fill in known information to equation:
X (calculated drip rate) = (1000mL x 15 drop/mL) / 60 minutes
X = 15000 drops (mL cancels out) / 60 min
X = 15000 drops / 60 minutes = 250 gtt/minute
Using the Parkland formula, you have calculated that you need to give 10L of Normal Saline to your patient over 8 hours. If you are using a 15-drop/mL drip set, what should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Total Volume (mL to be given): 10000mL
Drip Set: 15-drop/mL
Total Time: 8 hours
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Total Volume x Drip Set) / Total Time
Fill in known information to equation:
X (calculated drip rate) = (10000 mL x 15 drop/mL) / 8 hours
X = 150000 drops (mL cancels out) / 480 minutes
X = 150000 drops / 480 minutes = 312.5 gtt/minute
Dopamine:
- Dopamine is administered as a drip because it is a very potent drug that is only given to extremely sick patients. The effects of Dopamine on the body are dependent on the dose given. A dose of 5mcg/kg/min has different actions on the body than a dose of 20mcg/kg/min. An IV drip of Dopamine allows you to control the actions of the drug in the body as needed.
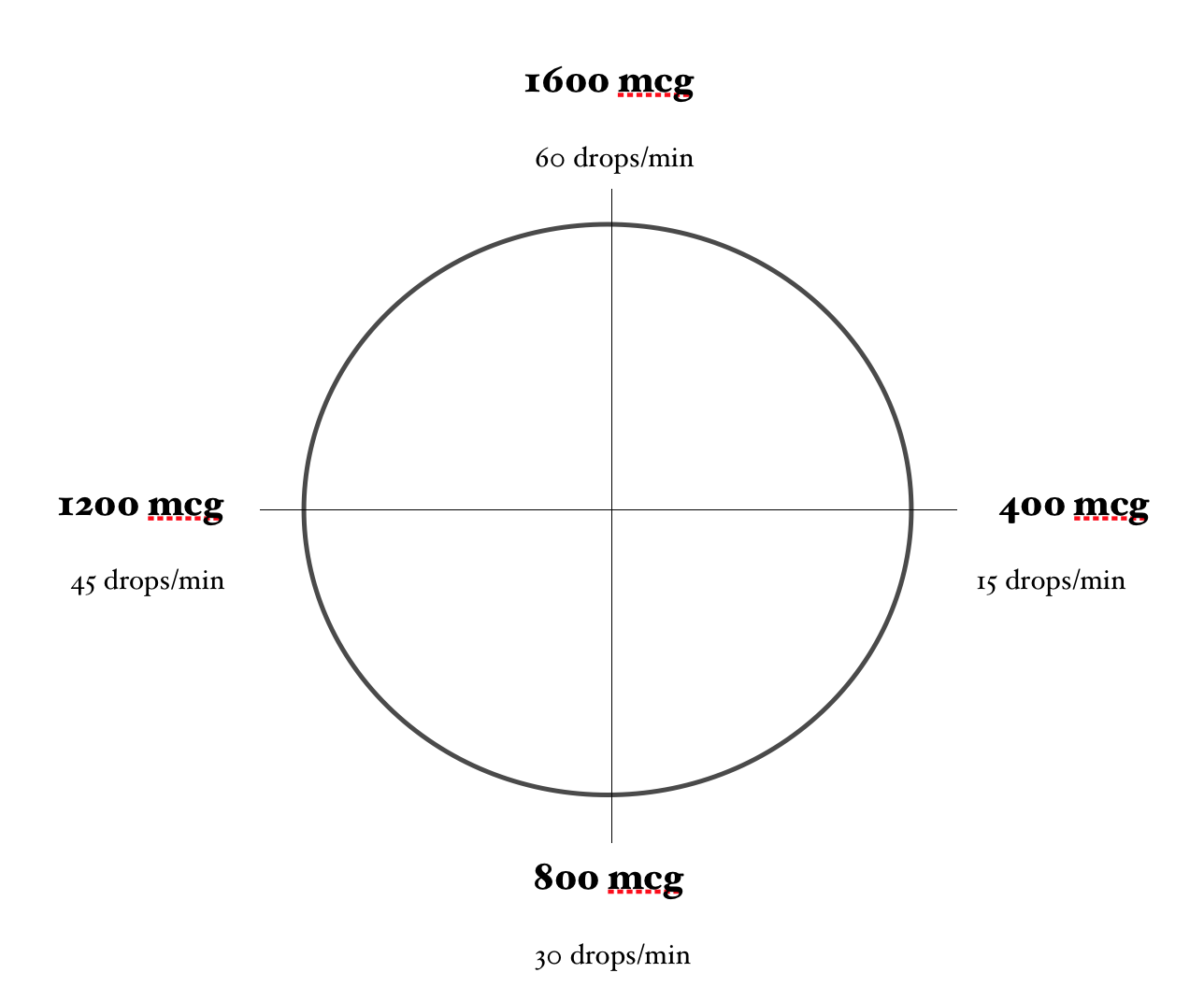
- When calculating Dopamine drip rates, your calculations should be based on a concentration of 1600mcg/mL. Premixed dopamine bags should come in this concentration. If you need to mix your own IV bag with Dopamine, it is important to achieve this concentration as well.
- Dopamine = 1600mcg/mL
Your medical kit only has a 250mL bag of Normal Saline in it. How much Dopamine do you need to inject into the bag to achieve the desired concentration of 1600mcg/mL?
Total Volume (mL of solution to be mixed with): 250mL
Desired dose: 1600mcg/mL
X: amount of Dopamine to be injected (mg)
(1600mcg/1mL) = (X/Total volume)
Fill in known information to equation and cross multiply. Then solve for X: 1600mcg / 1mL = X / 250 mL
X = 1600 x 250 (mL cancels out)
X = 400000mcg = 400mg
You should inject 400mg of Dopamine into the 250mL bag of Normal Saline to achieve the desired concentration of 1600mcg/mL.
There are two ways to calculate a Dopamine drip rate:
1. Use the drip rate formula and performing the mathematical operations to find the exact drip rate.
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
2. Use the Dopamine clock to quickly obtain a relatively accurate drip rate.
Calculating a Dopamine Drip… Using the Drip Rate Formula
- Your protocols indicate you should administer 10mcg/kg/min of Dopamine to your hypotensive patient. Your patient weighs 100kg. You have 400mg of Dopamine in 250mL of Normal Saline and are using a 60-dropmL drip set. What should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Desired Dose: 10mcg/kg/minute
Drip Set: 60-drop/mL
Drug Concentration: 400mg/250mL (1600mcg/mL)
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
Fill in known information to equation:
Desired dose = 10mcg/kg/minute X 100kg = 1000mcg/min
X (calculated drip rate) = (1000mcg/minute X 60-drop/mL) / 1600mcg/mL
X = 60000 (mcg & mL cancel out) / 1600
X = 60000 / 1600 = 37.5 gtt/minute
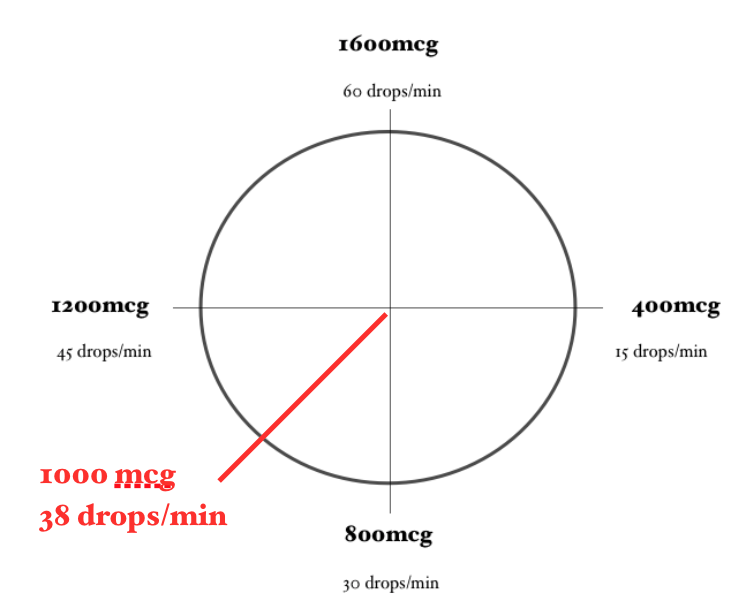
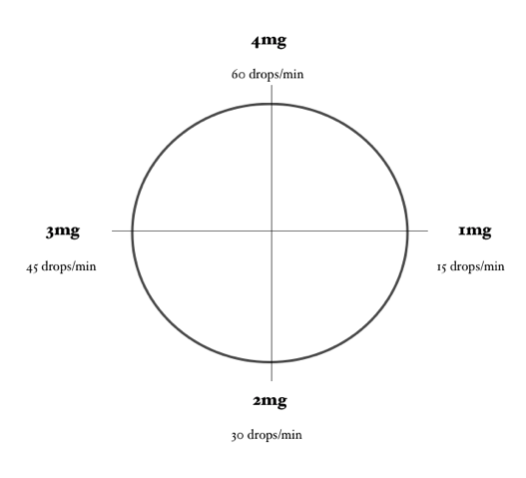
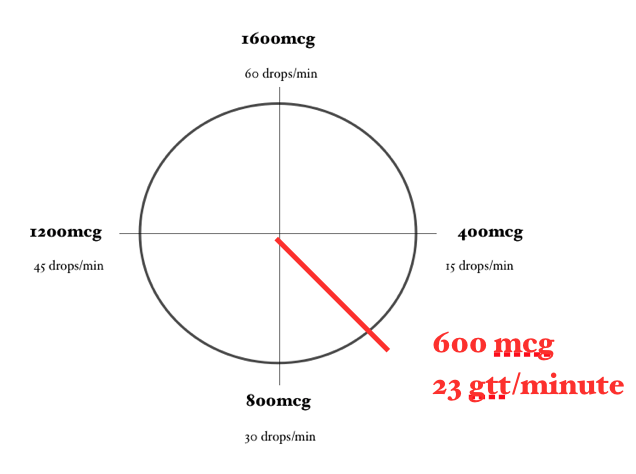
Calculating a Dopamine Drip… Using the Dopamine Clock
Using the same problem and the same numbers, let’s calculate this dopamine drip using the Dopamine Clock.
In order for the math to work properly, you need to ensure that the concentration of Dopamine you are using is 1600 mcg/mL (or you have adjusted your math to account for a different concentration) and you need to be using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Here is what we know:
Desired Dose: 10mcg/kg/minute
Patient Weight (in Kg): 100 kg
The Dopamine Clock is dosed as mcg/min so we need to get our math to show mcg/min. We can do this by multiplying the mcg/kg/minute dose by the patient’s weight (in Kg):
10mcg/kg/minute x 100kg = 1000mcg/minute (kg cancels out)
Now, locate on the clock approximately where 1000mcg/min would be. Then approximate how many drops/minute are required to achieve this dose.
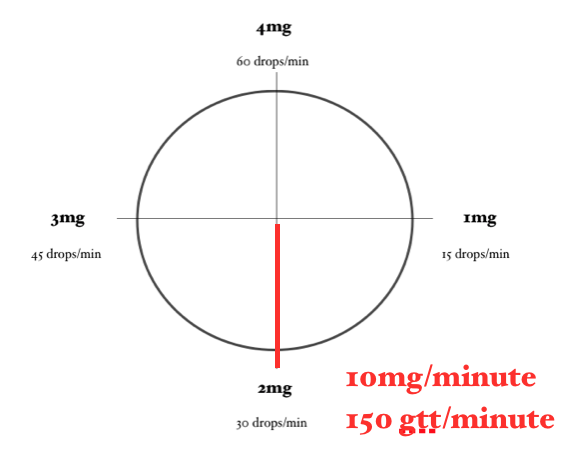
For example, a dose of 1000mcg/min would require approximately 38 gtt/minute.
Lidocaine:
- Lidocaine is given as a maintenance drip, after an initial bolus, in order to maintain the therapeutic dose in the patient’s bloodstream.
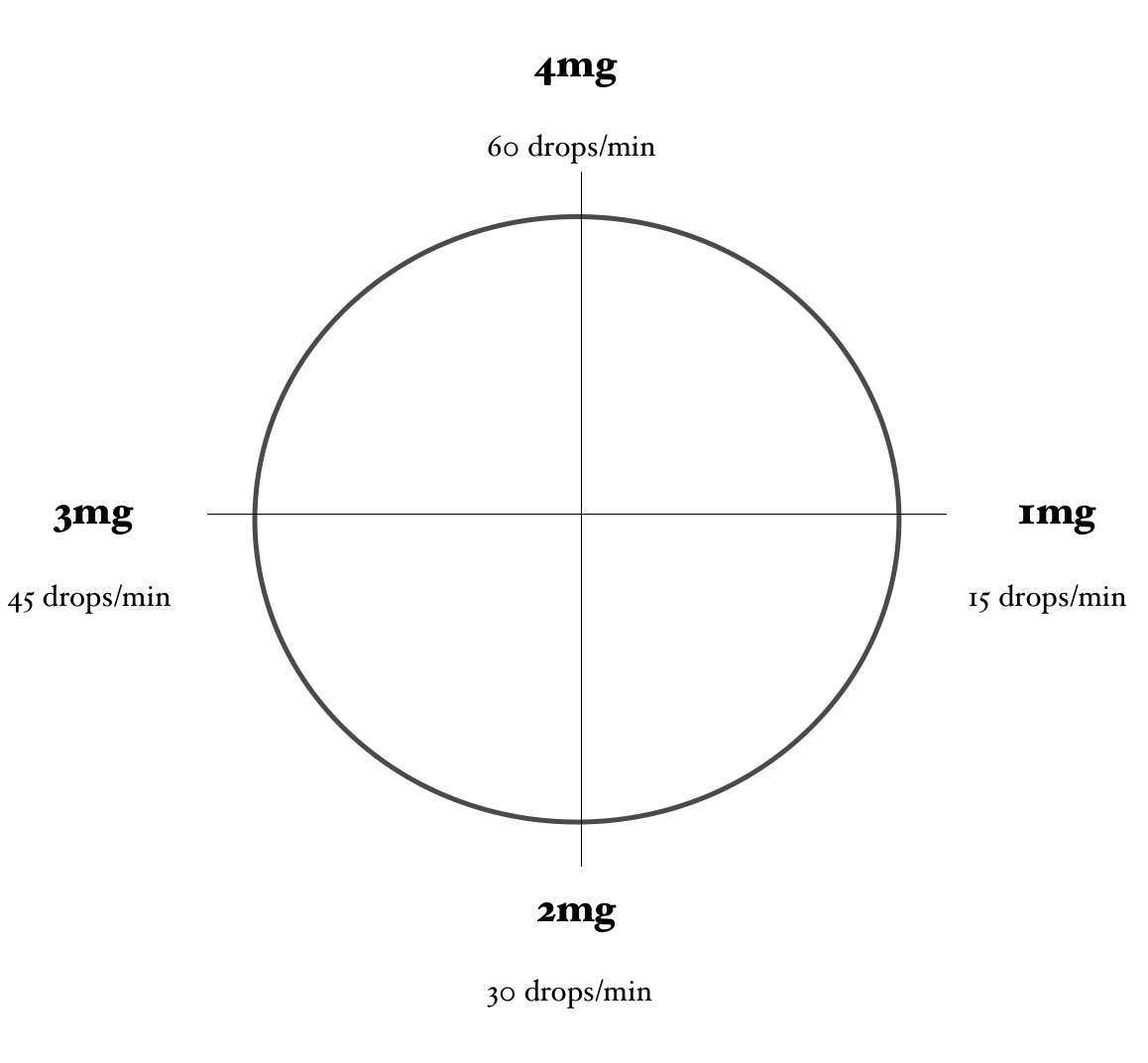
- When calculating Lidocaine drip rates, your calculations should be based on a concentration of 4mg/mL. Premixed Lidocaine bags should come in this concentration. If you need to mix your own IV bag with Lidocaine, it is important to achieve this concentration as well.
Lidocaine = 4mg/mL
Your medical kit only has a 1000mL bag of Normal Saline in it. How much Lidocaine do you need to inject in to the bag to achieve the desired concentration of 4mg/mL?
Total Volume (mL of solution to be mixed with): 1000mL
Desired dose: 4mg/mL
X: amount of Lidocaine to be injected (mg)
(4mg/1mL) = (X/Total Volume)
Fill in the known information into equation and cross multiply. Then solve for X:
4mg / 1mL = X / 1000mL
X = 4 x 1000 (mL cancels out)
X = 4000mg
You should inject 4000mg of Lidocaine into the 1000mL bag of Normal Saline to achieve the desired concentration of 4mg/mL.
There are two ways to calculate a Lidocaine drip rate:
1. Use the drip rate formula and perform the mathematical operations to find the exact drip rate.
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
2. Use the Lidocaine clock to quickly obtain a relatively accurate drip rate.
Calculating a Lidocaine Drip… Using the Drip Rate Formula
Your cardiac arrest patient has experienced return of spontaneous circulation. Protocol indicates you should start a Lidocaine drip at 1.5mg/minute. You have 2000mg of Lidocaine in 500mL of Normal Saline and are using a 60-dropmL drip set. What should your flow rate be (gtt/min)?
Desired Dose: 1.5mg/minute
Drip Set: 60-drop/mL
Drug Concentration: 2000mg/500mL (4mg/mL)
Calculated drip rate: X
X = (Desired Dose x Drip Set) / Drug Concentration
Fill in known information into the equation:
X (calculated drip rate) = (1.5mg/minute x 60-drop/mL) / 4mg/mL
X = 90 (mg & mL cancel out) / 4
X = 90 / 4 = 22.5 gtt/minute
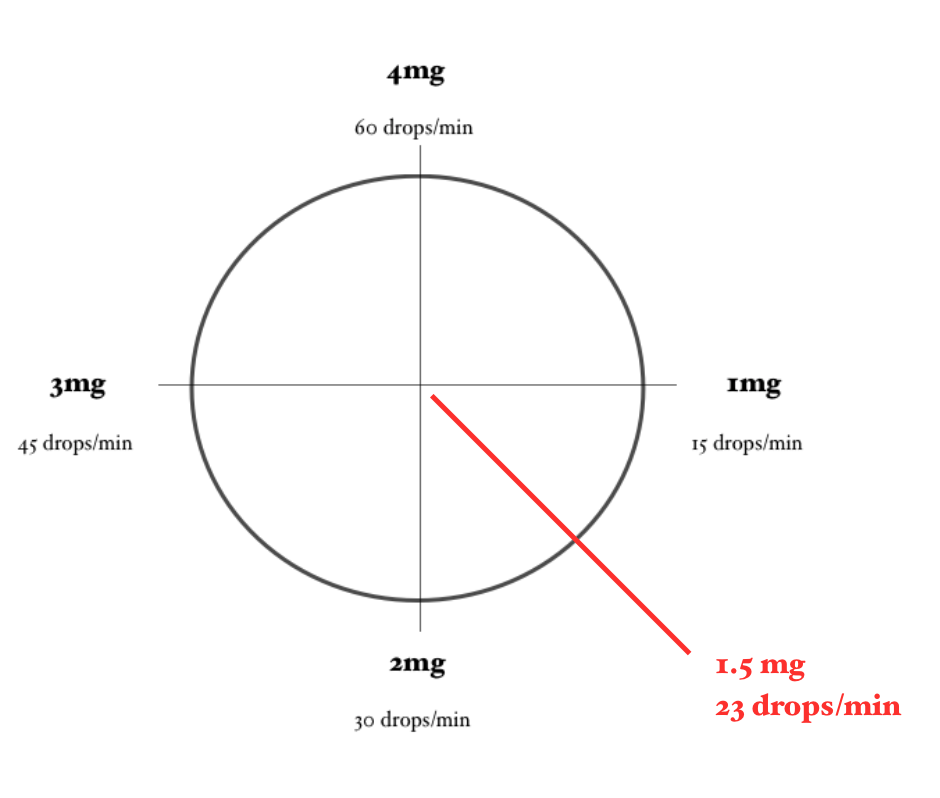
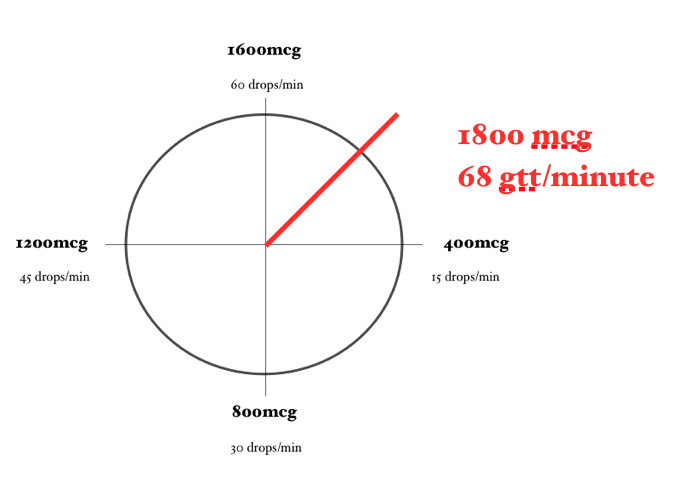
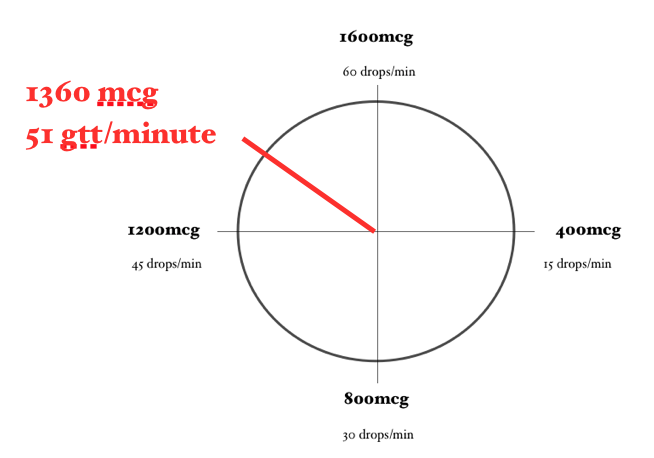
Calculating a Lidocaine Drip… Using the Lidocaine Clock
Using the same problem and the same numbers, let’s calculate this Lidocaine drip using the Lidocaine Clock.
In order for the math to work properly, you need to ensure that the concentration of Lidocaine you are using is 4 mg/mL (or you have adjusted your math to account for a different concentration) and you need to be using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Here is what we know:
Desired Dose: 1.5 mg/minute
Now locate on the clock approximately where 1.5mg/minute would be. Then, approximate how many drops/minute are required to achieve this dose.
For example, a dose of 2mg/min would require approximately 23 gtt/minute.
Med Math 101: Practice Problems
Below are a series of practice problems meant to increase your proficiency and test your understanding of what you have just learned.
Metric System
- Convert 8.4 L to mL =
- Convert 1274 g to Kg =
- Convert 111.4 g to mg =
- Convert 1350 mcg to g =
- Convert 125 mL to L =
Pounds to Kilograms
- 40 lbs =
- 180 lbs =
- 220 lbs =
- 260 lbs =
- 350 lbs =
Kilograms to Pounds
- 4 kg =
- 50 kg =
- 70 kg =
- 120 kg =
- 135 kg =
Medication Concentrations
- 4mg/2mL =
- 1mg/10mL =
- 250mcg/5mL =
- 50g/500mL =
- 150mg/250mL =
- 30mg/30mL =
- 200mg/10mL =
- 1g/10mL =
- 50mEq/50mL =
- 100mg/25mL =
Bolus Medications
- Administer 75mcg Fentanyl citrate (concentration of 250mcg/5mL).
- Administer 15g Dextrose 10% (concentration of 50g/500mL).
- Administer 0.16mg Atropine (concentration 1mg/10mL).
- Administer 12.5mg Promethazine (concentration of 25mg/mL).
- Administer 4g of Magnesium Sulfate (concentration of 1g/2mL).
- Administer 0.4mg of Nitroglycerin (concentration of 400mcg/tab).
- Administer 18mg of Morphine sulfate (concentration of 5mg/mL).
- Administer 25mg of Diphenhydramine (concentration of 50mg/2mL).
- Administer 100mg of Suxamethonium chloride (concentration of 200mg/20mL).
- Administer 24mg of Etomidate (concentration of 20mg/10mL).
IV Drips (answer in gtt/minute)
- Administer 70mcg/min Nitroglycerin (concentration of 200mcg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 200mg/hour Morphine sulfate (concentration of 5mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 50mg/hour Lidocaine (concentration 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 1.5mg/min Amiodarone (concentration of 3mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 4g of Magnesium Sulfate over 5 minutes (concentration of 400mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 5mcg/minute of Epinephrine (concentration of 4mcg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 25mg/hour Versed (concentration of 500mcg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 1g/hour Cefazolin sodium (concentration of 1000mg/500mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Is this drip rate possible to achieve?
- Administer 0.5mg/minute Diazepam (concentration of 30mg/L) using a 10-drop/mL drip set. Is this drip rate possible to achieve?
- Administer 300mg/hour Labetalol (concentration of 2.5g/500mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Fluid Administration (answer in gtt/minute)
- Administer 125mL/hour using a 15-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 350mL/hour using a 15-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 500mL/hour using a 10-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 50mL/hour using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 1000mL/hour using a 10-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 80mL/hour using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 1.875L/hour using a 10-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 940mL/hour using a 15-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 43mL/hour using a 10-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 17mL/hour using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Dopamine Drips (answer in gtt/minute)
- Administer 5mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 400mg/250mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 75 kg.
- Administer 17mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 1600mcg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 55 kg.
- Administer 10mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 0.8g/500mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 125 kg.
Lidocaine Drips (answer in gtt/minute)
- Administer 3.5mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 1.2mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
- Administer 5mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Dopamine Clock (answer in gtt/minute – draw line on clock)
- Administer 7.5mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 400mg/250mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 80 kg.
2. Administer 12mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 1600mcg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 150 kg.
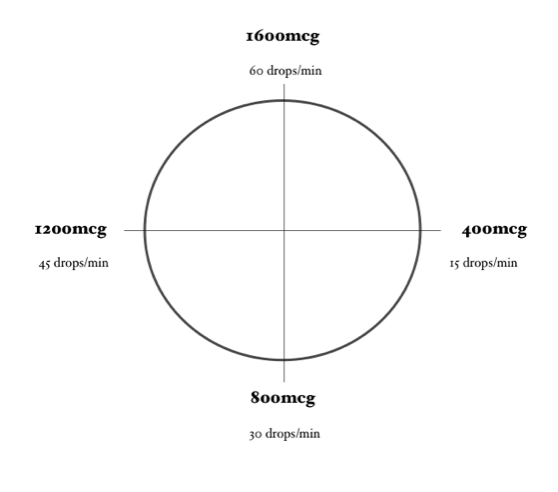 3. Administer 20mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 0.8g/500mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 68 kg.
3. Administer 20mcg/kg/minute Dopamine (concentration of 0.8g/500mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set. Your patient weighs 68 kg.
Lidocaine Clock (answer in gtt/minute – draw line on clock)
- Administer 10mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
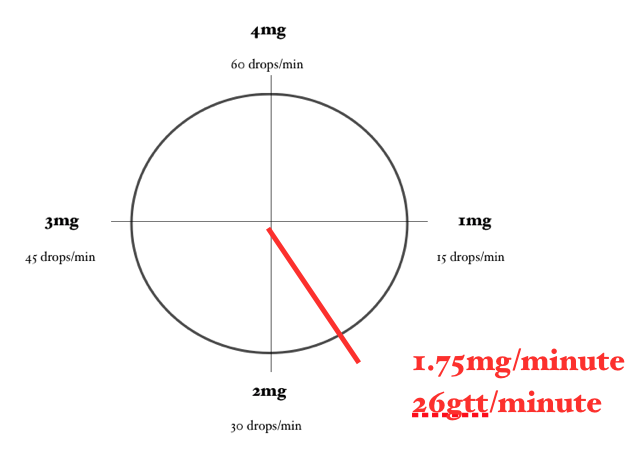
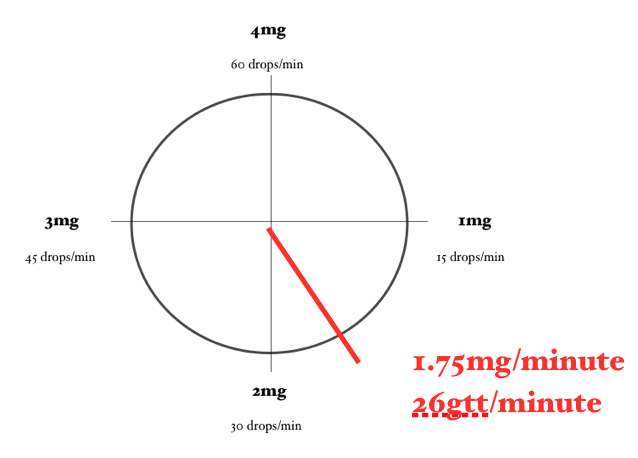
2. Administer 1.75mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
3. Administer 1.5mg/minute Lidocaine (concentration of 4mg/mL) using a 60-drop/mL drip set.
Med Math 101: Practice Problems
ANSWERS
Metric System
- 8400 mL
- 1.274 kg
- 111400 mg
- 0.00135 g
- 0.125 L
Pounds to Kilograms
- 18 kg
- 81 kg
- 99 kg
- 117 kg
- 157.5 kg
Kilograms to Pounds
- 8.8 lbs
- 110 lbs
- 154 lbs
- 264 lbs
- 297 lbs
Medication Concentrations
- 2mg/mL
- 0.1mg/mL (100mcg/mL)
- 50mcg/mL
- 0.1g/mL (100mg/mL)
- 0.6mg/mL (600mcg/mL)
- 1mg/mL
- 20mg/mL
- 0.1g/mL (100mg/mL)
- 1mEq/mL
- 4mg/mL
Bolus Medications
- 1.5mL
- 150mL
- 1.6mL
- 0.5mL
- 8mL
- 1 tab
- 3.6mL
- 1mL
- 10mL
- 12mL
IV Drips
- 21 gtt/min
- 40 gtt/min
- 12.5 gtt/min
- 30 gtt/min
- 120 gtt/min
- 75 gtt/min
- 50 gtt/min
- 500 gtt/min; no
- 1000 gtt/min; no
- 60 gtt/min
Fluid Administration
- 31 gtt/min
- 88 gtt/min
- 83 gtt/min
- 50 gtt/min
- 167 gtt/min
- 80 gtt/min
- 313 gtt/min
- 235 gtt/min
- 7 gtt/min
- 17 gtt/min
Dopamine Drips
- 14 gtt/minute
- 35 gtt/minute
- 47 gtt/minute
Lidocaine Drips
- 53 gtt/minute
- 18 gtt/minute
- 75 gtt/minute
Dopamine Clock
Lidocaine Clock
- 10mg/minute (2.5 times more than concentration so 2.5 times around the clock)
2. 75mg/minute (a little less than half of the concentration so a little less than halfway around the clock)
3. 4.5mg/minute (just a little more than the concentration so just a little more than one whole time around the clock)
- Dozens of courses and topics
- State-specific requirements
- We report to CAPCE in real time